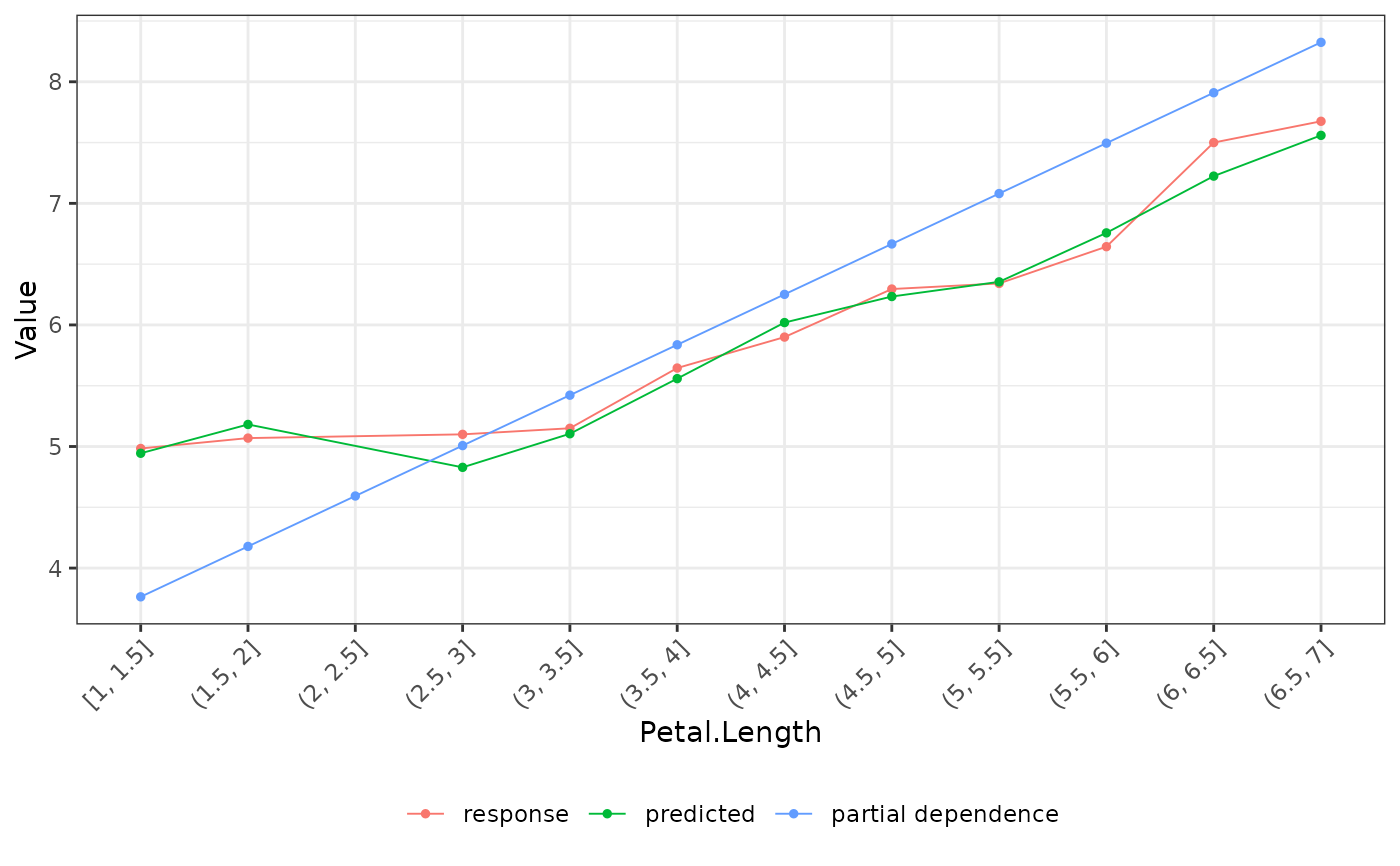
Combination of Response, Predicted, Partial Dependence, and ALE profiles.
Source:R/light_effects.R
light_effects.RdCalculates response- prediction-, partial dependence, and ALE profiles of a
(multi-)flashlight with respect to a covariable v.
light_effects(x, ...)
# Default S3 method
light_effects(x, ...)
# S3 method for class 'flashlight'
light_effects(
x,
v,
data = NULL,
by = x$by,
stats = "mean",
breaks = NULL,
n_bins = 11L,
cut_type = c("equal", "quantile"),
use_linkinv = TRUE,
counts_weighted = FALSE,
v_labels = TRUE,
pred = NULL,
pd_indices = NULL,
pd_n_max = 1000L,
pd_seed = NULL,
ale_two_sided = TRUE,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'multiflashlight'
light_effects(
x,
v,
data = NULL,
breaks = NULL,
n_bins = 11L,
cut_type = c("equal", "quantile"),
...
)Arguments
- x
An object of class "flashlight" or "multiflashlight".
- ...
Further arguments passed to
formatC()in forming the cut breaks of thevvariable.- v
The variable name to be profiled.
- data
An optional
data.frame.- by
An optional vector of column names used to additionally group the results.
- stats
Deprecated. Will be removed in version 1.1.0.
- breaks
Cut breaks for a numeric
v. Used to overwrite automatic binning vian_binsandcut_type. Ignored ifvis not numeric.- n_bins
Approximate number of unique values to evaluate for numeric
v. Ignored ifvis not numeric or ifbreaksis specified.- cut_type
Should a numeric
vbe cut into "equal" or "quantile" bins? Ignored ifvis not numeric or ifbreaksis specified.- use_linkinv
Should retransformation function be applied? Default is
TRUE.- counts_weighted
Should counts be weighted by the case weights? If
TRUE, the sum ofwis returned by group.- v_labels
If
FALSE, return group centers ofvinstead of labels. Only relevant ifvis numeric with many distinct values. In that case useful for instance when different flashlights use different data sets.- pred
Optional vector with predictions (after application of inverse link). Can be used to avoid recalculation of predictions over and over if the functions is to be repeatedly called for different
vand predictions are computationally expensive to make. Not implemented for multiflashlight.- pd_indices
A vector of row numbers to consider in calculating partial dependence profiles and "ale".
- pd_n_max
Maximum number of ICE profiles to calculate (will be randomly picked from
data) for partial dependence and ALE.- pd_seed
Integer random seed used to select ICE profiles for partial dependence and ALE.
- ale_two_sided
If
TRUE,vis continuous andbreaksare passed or being calculated, then two-sided derivatives are calculated for ALE instead of left derivatives. More specifically: Usually, local effects at value x are calculated using points in \([x-e, x]\). Setale_two_sided = TRUEto use points in \([x-e/2, x+e/2]\).
Value
An object of class "light_effects" with the following elements:
response: A tibble containing the response profiles. Column names can be controlled byoptions(flashlight.column_name).predicted: A tibble containing the prediction profiles.pd: A tibble containing the partial dependence profiles.ale: A tibble containing the ALE profiles.by: Same as inputby.v: The variable(s) evaluated.
Details
Note that ALE profiles are being calibrated by (weighted) average predictions. The resulting level might be quite different from the one of the partial dependence profiles.
Methods (by class)
light_effects(default): Default method.light_effects(flashlight): Profiles for a flashlight object.light_effects(multiflashlight): Effect profiles for a multiflashlight object.
See also
Examples
fit_lin <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ ., data = iris)
fl_lin <- flashlight(model = fit_lin, label = "lin", data = iris, y = "Sepal.Length")
# PDP, average response, average predicted by Species
eff <- light_effects(fl_lin, v = "Petal.Length")
plot(eff)
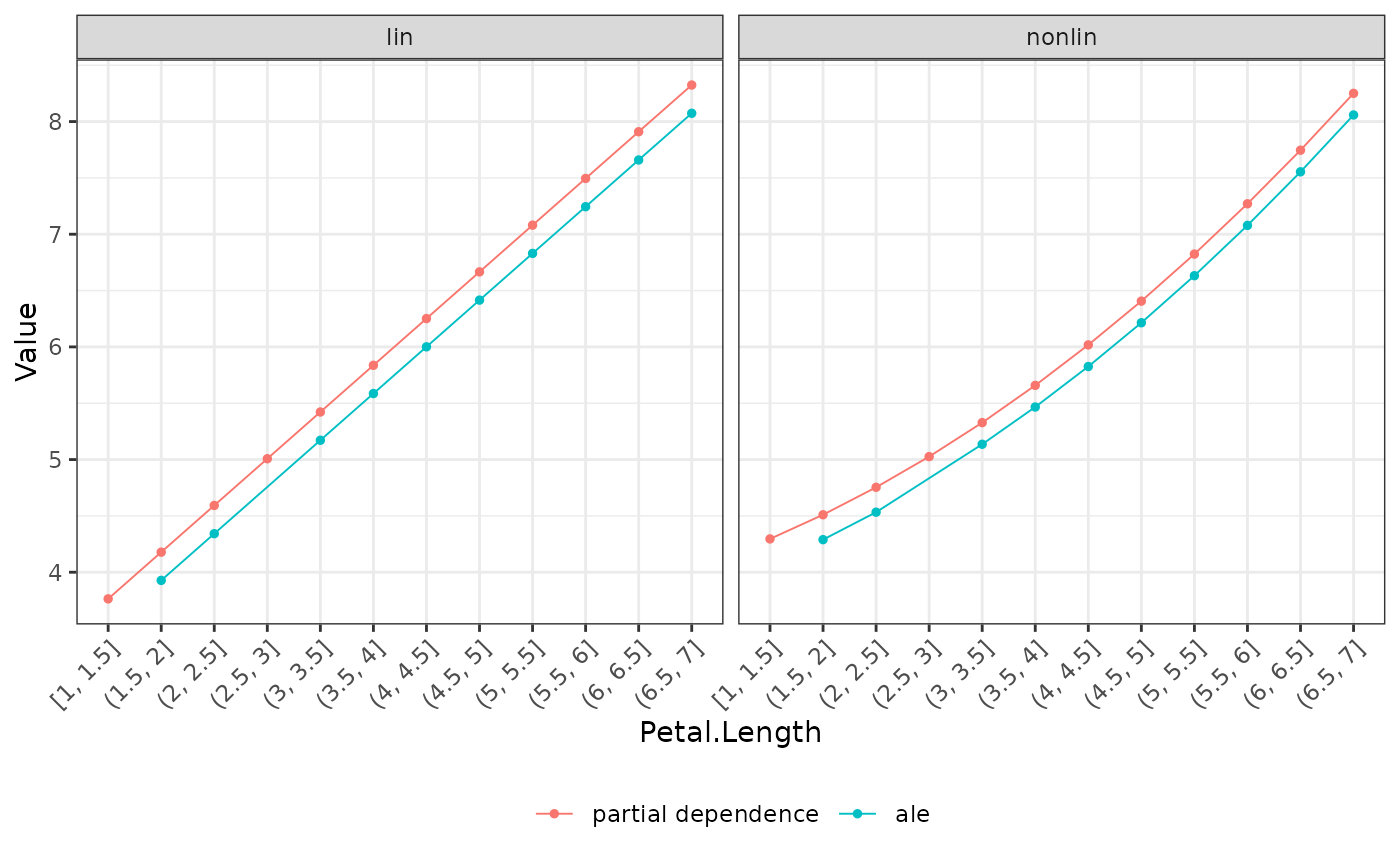
 # PDP and ALE
plot(eff, use = c("pd", "ale"), recode_labels = c(ale = "ALE"))
# PDP and ALE
plot(eff, use = c("pd", "ale"), recode_labels = c(ale = "ALE"))
 # Second model with non-linear Petal.Length effect
fit_nonlin <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ . + I(Petal.Length^2), data = iris)
fl_nonlin <- flashlight(
model = fit_nonlin, label = "nonlin", data = iris, y = "Sepal.Length"
)
fls <- multiflashlight(list(fl_lin, fl_nonlin))
# PDP and ALE
plot(light_effects(fls, v = "Petal.Length"), use = c("pd", "ale"))
# Second model with non-linear Petal.Length effect
fit_nonlin <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ . + I(Petal.Length^2), data = iris)
fl_nonlin <- flashlight(
model = fit_nonlin, label = "nonlin", data = iris, y = "Sepal.Length"
)
fls <- multiflashlight(list(fl_lin, fl_nonlin))
# PDP and ALE
plot(light_effects(fls, v = "Petal.Length"), use = c("pd", "ale"))